How BitHide Protects Businesses from Hacks: Technology Overview
How to protect your business from hacks and tracking with BitHide.

Cryptocurrencies are often thought of as anonymous, but in reality, public blockchain explorers can trace the movement of funds, and IP addresses can reveal the geolocation of the server and the wallet owner through OSINT. Naturally, attackers use this. According to Chainalysis, in the first half of 2025, losses from hacks, phishing, and fraud exceeded $2.2 billion — nearly the same as for the entire year of 2024.
Businesses are attackers’ main focus. Hackers monitor real company turnover and then look for vulnerabilities — and there are plenty: custodial solutions, unlimited employee access, and the human factor. From there, it’s only a short step to wallet breaches, theft of funds, or even kidnapping of crypto owners. That’s why it’s especially important for companies to choose a reliable crypto payment solution to handle finances.
Below we’ll explain how the BitHide business wallet protects your infrastructure.
Protection Against Transaction Tracking
The blockchain is a transparent ledger where every transaction leaves a trace: IP address, metadata, behavioral patterns. Hackers use this to deanonymize businesses, track cash flows, and link wallets to real people.
Attackers don’t strike randomly. They deliberately hunt the most profitable targets, gathering as much information as possible before launching an attack.
For businesses, protection against tracking is critical. BitHide restores privacy to crypto operations using Dark Wing technology: it hides the wallet’s IP address, employs one-time addresses for aggregation and transfers, and uses temporary Gas Stations to pay blockchain fees.
IP Address Protection
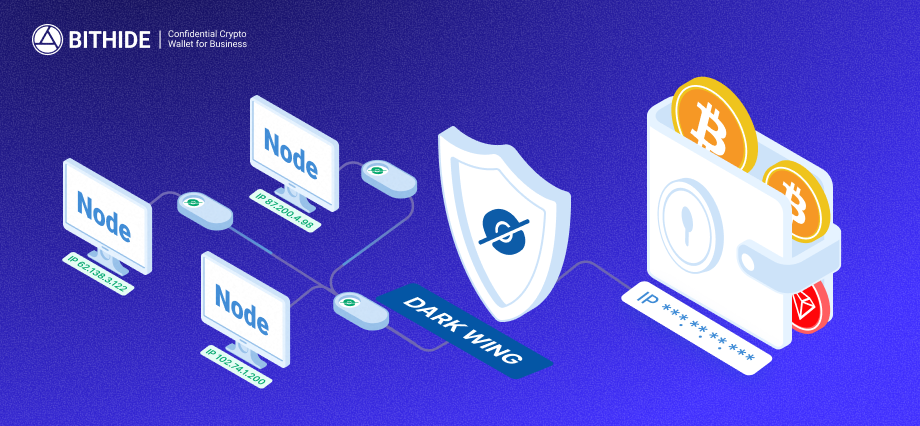
One of the most vulnerable signals is the wallet’s real IP address. It hits the node every time a transaction is initiated. Many nodes are controlled by attackers, who can use the IP address to determine the server’s geolocation and the wallet owner’s identity via OSINT. Once that’s known, tracking someone down in real life is only a matter of time — and attackers will try, especially if they see large sums moving through the wallet.
This is exactly how many targeted attacks begin. For example, in May 2025, 28-year-old crypto millionaire Michael Carturan was tracked and kidnapped. He was held for 17 days while attackers demanded access to his wallets. Believing he had about $28 million in his accounts, they tortured him — using electric shocks and even threatening him with a chainsaw.
To protect real IP addresses, BitHide uses Tor and VPN simultaneously. Tor changes the IP address, while the VPN ensures stable connections to the node, which ultimately receives a repeatedly altered IP. This happens for every transaction. Identifying the real IP becomes nearly impossible, making it extremely difficult to uncover the server’s or owner’s location.
Temporary Addresses for Paying Fees
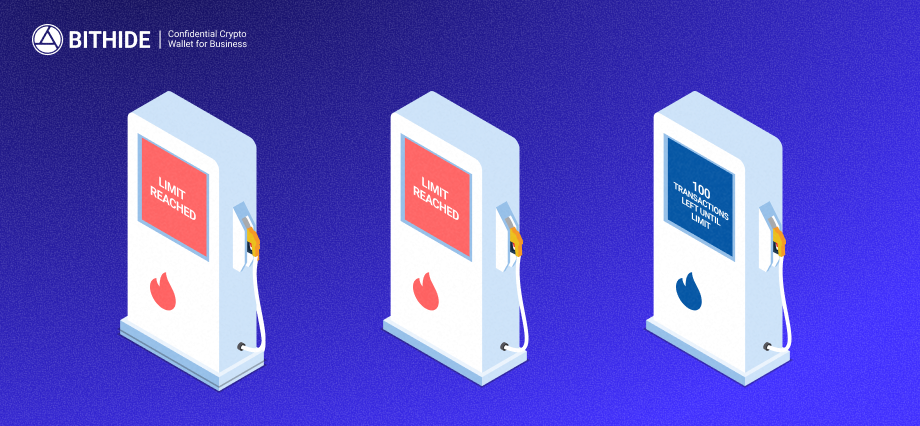

When a business repeatedly pays blockchain fees from the same address, attackers can detect patterns, cluster addresses, and link them back to the wallet.
Case Study: Hack
This is how hackers exposed an iGaming company processing payouts on the TRON network. They noticed that roughly 12,000 TRX were deducted weekly from a single address to cover fees. By analyzing linked wallets, attackers reconstructed the full transaction chain and estimated the company’s monthly turnover.
The company was using a custodial crypto service, meaning private keys were stored with a third-party provider (the custodian). Hackers carried out a phishing attack against the provider’s employees, gained access to internal systems, and from there to the company’s private keys. Within a month, they drained $300,000 in USDT.
With BitHide, this risk is eliminated. Fees are paid through Gas Stations — temporary addresses with user-defined limits on transaction count. Once the limit is reached, the station is retired and automatically replaced with a fresh one, unlinked to the previous. This makes clustering all of a business’s transactions and calculating its turnover extremely difficult.
Proxy Payments for Aggregation and Withdrawals
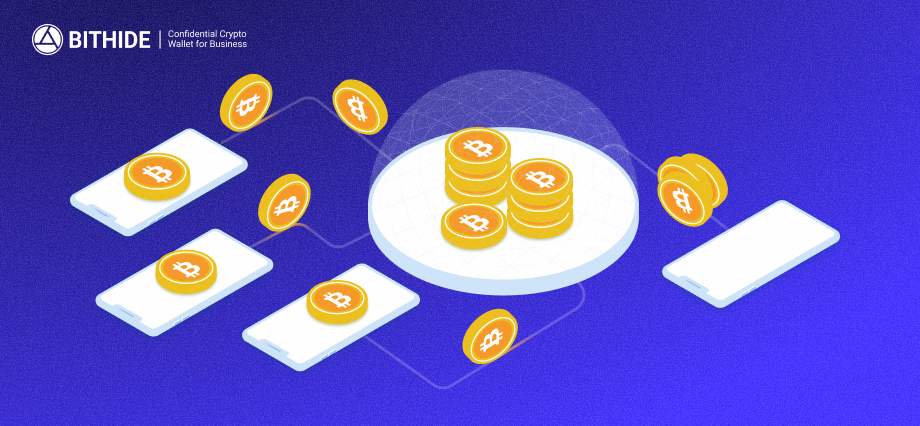

When thousands of micro-deposits are continuously funneled into a single address, that address becomes a window through which attackers can monitor a company’s turnover and decide whether it’s a worthwhile target.
Case Study: Hack
In 2024, hackers exposed the payment infrastructure of an iGaming platform this way: they made a test $30 deposit, identified its central address, and observed that it processed up to 4,000 transactions daily, totaling more than $10 million per month. A wallet handling such volume was a prime target, so attackers invested time and resources into finding a way in. Ultimately, they mapped all incoming flows, planned their attack, and inflicted over $130,000 in losses.
BitHide eliminates this vulnerability. Clients can use Proxy Payments, where user-defined amounts are automatically gathered from multiple wallet addresses onto a one-time address, then sent in a single transaction either to a counterparty or to another internal address for further management. This removes the need for a single central address to collect micro-payments, making it impossible to calculate business turnover.
Protection Against Hacks
To prevent clustering and turnover tracking, BitHide deploys Dark Wing technology. But it also includes additional architectural elements that strengthen wallet security:
Non-Custodial Architecture
BitHide is a non-custodial wallet, meaning funds remain fully under your control. We never store client private keys or seed phrases, and we cannot access them.
Multi-Factor Authentication
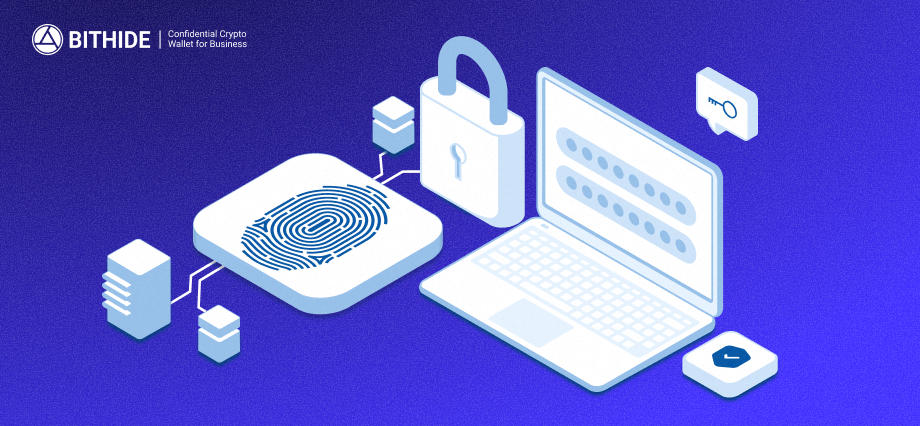

Private keys are encrypted, and login requires a combination of server address, email, username, secret key, PIN code, and optionally 2FA, which includes Google Authenticator and fingerprint recognition. BitHide remembers previously used devices, and if a new one connects, additional verification is required.
Encrypted Wallet Backups
In case of emergencies, the full transaction history is backed up in real time and stored in the client’s cloud — encrypted with AES-256. No known technology today can break such encryption, so only the wallet owner can decrypt the backup.
Callback Hashing
When a business connects its wallet to a CRM, platforms, or payment pages, every successful transaction triggers a callback. This notification tells the company’s server that the payment has gone through. If an attacker intercepts or forges such a message, they could simulate a successful payment and gain access to goods, services, or even trigger an automatic payout.
BitHide solves this with signed callbacks: each callback notification can include a hash signature created with a secret key stored only on your server. Upon receiving the callback, the system verifies the signature and rejects any unsigned or fake messages.
This mechanism is used in BitHide’s API integrations and protects businesses from MITM attacks and data tampering, even if HTTPS traffic is compromised.
Protection Against Social Engineering and Phishing
The most dangerous and common attacks in crypto rely on social engineering, tricking victims into handing over wallet access. Fake websites, impersonated support staff, spoofed emails, and chat scams — the methods constantly evolve, and even experienced employees may not recognize an attack in time.
Even large players aren’t immune. In May 2025, hackers bribed overseas support staff and gained access to Coinbase’s customer database. Earlier, in February 2025, they compromised a Bybit manager’s account, stealing $1.5 million.
Businesses are also threatened by “drainers.” In 2024 alone, over $494 million was stolen through such schemes. In one case, attackers faked a Coinbase Wallet login page. A company employee connected a corporate wallet and signed an “empty” transaction containing approve(spender, type(uint256).max) in the code. Within a minute, nearly $120,000 in USDC was drained, and the business lost control over its liquidity pool.
Companies are especially vulnerable because they employ many people — and a single mistake can compromise the entire infrastructure, leading to catastrophic financial losses.
BitHide addresses these risks at the infrastructure level.
Roles and Permissions
To prevent such scenarios, BitHide implements a multi-layer Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) model. Each user can be assigned a role and permission set:
- Some may only view balances.
- Others may initiate transactions.
- Others may run AML checks, create wallets, or manage Gas Stations.
Additionally, dual confirmation is required: all withdrawal operations must be approved by another user with the proper rights. Even if one account is compromised, the transaction won’t go through without additional approval.
BitHide also logs every employee action with timestamps and device details. Any attempt to exceed assigned permissions is recorded and can be immediately blocked by an administrator.
This approach not only prevents data leaks but also allows rapid incident localization if something does occur.
Conclusion
The blockchain doesn’t forgive mistakes: one leaked IP address, a single collection address, or unlimited employee access — and a business could lose millions. BitHide eliminates these risks at every level: it hides network metadata and IP addresses, protects against phishing and callback tampering, and ensures private keys and seed phrases always remain solely with you.
Request a BitHide demo and see how to reliably protect your business from hacks, theft, social engineering, and phishing.


